Very high filtration rates. Due to the depth filtration of the free-fiber cloth. TSS concentrations below 10 mg/l expected at discharge, depending on application.
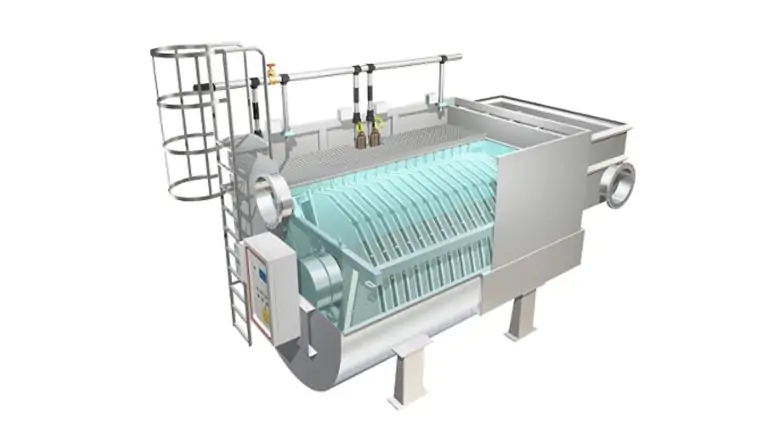
Pile Cloth Filters
for tertiary wastewater treatment
Very high solids removal yields and minimal product life-cycle cost: these are the advantages of free-fiber cloth filters for tertiary filtration. These are filtration systems suitable for industrial wastewater, civil wastewater and, in some cases, first rainwater.
Reduced energy use. Gravity filtration, power consumption only in backwash phase.
Operational continuity. Filtration is continuous during counter-current cloth washing.
Flexibility with different loads. Excellent tolerance to hydraulic variations and fluctuations in input loads.
Simple Maintenance. Simplicity and reduced frequency of intervention.
Minimum life-cycle cost. Low investment costs (CAPEX), maintenance and resource utilization costs (OPEX) result in optimal return on investment.
Pile Cloth Filters: description
Wastewater treatment plant operators have requirements such as improving the final quality of the effluent, adapting plants to new operating conditions, and recovering water for industrial or agricultural use. Precisely for the solution of these problems, MITA Water Technologies offers an effective and simple cloth filtration system: pile cloth filters, or free-fiber cloth filters, or else pile cloth media filters, for tertiary wastewater treatment.
Pile cloth media filters combine the surface filtration typical of microgrid systems with the depth filtration of sand filters (similar in operation and performance in terms of suspended solids removal). All with extremely low investment, operation and maintenance costs.
The construction concept of cloth media filters allows backwashing during operation, without stopping the machine, and thus filtration, and allows for minimal pressure drop (max 0.5 m w.g.), reduced energy use, and minimal footprint. Cloth filters consist of a support structure (drum or disc), covered with a special filtering cloth: these are synthetic fibers. The filters are equipped with a device for backwashing the cloths controlled by level sensors.
Several models are available with capacities up to 1,500 m3/h for a single filter unit.
Ask for Information
Pile Cloth Filters: Applications
Learn about installation contexts hereDownloads
Standard Components on all MITA Pile Cloth Filters

Free-Fiber Cloths
Cloth pile type: classic 10, micro 5 and others in development.

Cloth Backwashing
As the solids deposit on the cloth increases, the hydraulic resistance increases: having reached a difference of 15 ÷ 20 cm between the water inlet and outlet levels, the process of cleaning the cloth is automatically activated by the countercurrent passage, through the cloth, of the already filtered water sucked by the pumps. Minimal energy costs.

Disc or Drum Filters
The cloth filter consists of either a drum or filter discs (2 to 32), mounted on a hollow central shaft: discs and drum work completely submerged in the water to be treated. Filtration takes place by gravity, from outside to inside, with the machine stopped.
Our Range of Pile Cloth Filters

Drum Filters TF – TF VM
The high filtration rates and small footprint make the Drum Filter the ideal final filtration system for sewage treatment plants, industrial or municipal plants of small capacity. All units are complete with an electrical control panel and can be installed in a concrete tank or supplied complete with a metal containment tank.
Disc Filters PEC – PEC VM
With these free-fiber filtration systems, we get to serve medium to large sewage treatment plants with minimal floor space requirements. Not only that. In the PEC and PEC VM disc filters, backwashing with sequentially driven pumps provides the machine with operational continuity in wastewater treatment, consequently avoiding the need to provide a back-up unit.
Disc Filters PPC – PPC VM
A solution for high filtration rates and efficient handling and backwashing, with low installed power: PPC and PPC VM disc filters are for concrete or metal tank, respectively. All while maintaining flexibility with different loads and continuity of operation, typical of MITA pile cloth filters.
Vertical-Axis Disc Filters PECV VM
An optimal solution for small and medium-sized plants, as much for its compactness as for its simplicity of installation and operation: these are the PECV VM metal tank vertical axis disc filters, for the final separation of suspended solids from civil and industrial wastewater.Pile cloth filters: available versions

Basic Version
Backwash works with only one pump at a time-an additional energy saver.

HD version
Backwash works with one or two pumps at a time: great versatility of operation.

FHD Version
Backwash works with only two pumps at a time: fast and efficient tele-washing.
Some Projects with Pile Cloth Filters
Cloth Filters and Cooling Towers for Plastic Industry
Cooling and wastewater treatment together: that's the card that proved successful in supporting a plastics equipment company in northern Italy, which was already working with MITA Cooling Technologies (now a commercial partner of MITA Water Technologies). The possibility of water reuse, through comprehensive management of this resource, is a card that industries can exploit to derive value from blue gold.
Read moreCloth Filters for the Cuma Wastewater Treatment Plant
It is one of the largest tertiary filtration systems in Europe: the MITA supply for the vast Cuma water treatment plant near Naples, having a treatment capacity of 1,200,000 population equivalents. The goal of the project was to improve the plant's purification performance.
Read moreWould you like a noncommittal consultation?
Tell us about your project in wastewater treatment or tertiary filtration.
Contact us nowWhat is your process goal?
Tools to help you choose
Industrial and civil wastewater treatment technologies
Our support throughout the product life cycle
A sustainable and efficient solution for every industry and need
Resources
Needs of wastewater treatment
Discover the solution for all needsComparing different technologies
Find out all the different technologiesFind out more
All technical articlesOr You Can Choose
Our Newsletter
Sign up for the MITA Water Technologies newsletter: stay up-to-date on systems for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment and filtration.
